ArangoDB v2.8 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent version here: Try latest
Fluent AQL Interface
This chapter describes a fluent interface to query your graph. The philosophy of this interface is to select a group of starting elements (vertices or edges) at first and from there on explore the graph with your query by selecting connected elements.
As an example you can start with a set of vertices, select their direct neighbors and finally their outgoing edges.
The result of this query will be the set of outgoing edges. For each part of the query it is possible to further refine the resulting set of elements by giving examples for them.
Examples will explain the API on the social graph:
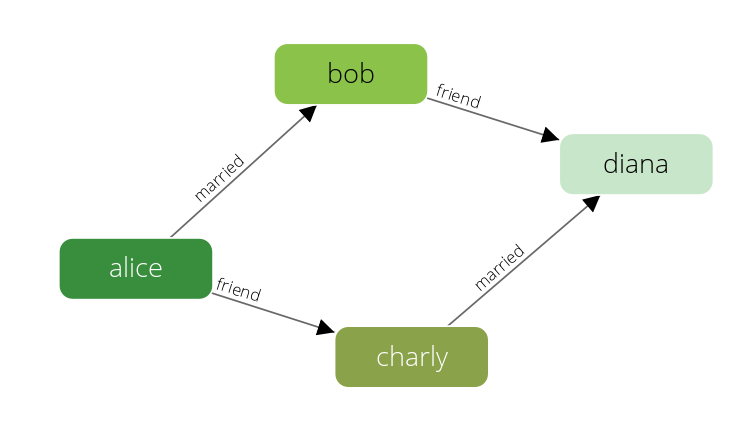
Definition of examples
For many of the following functions examples can be passed in as a parameter.
Examples are used to filter the result set for objects that match the conditions.
These examples can have the following values:
- null, there is no matching executed all found results are valid.
- A string, only results are returned, which _id equal the value of the string
- An example object, defining a set of attributes. Only results having these attributes are matched.
- A list containing example objects and/or strings.
All results matching at least one of the elements in the list are returned.
Starting Points
This section describes the entry points for the fluent interface. The philosophy of this module is to start with a specific subset of vertices or edges and from there on iterate over the graph.
Therefore you get exactly this two entry points:
- Select a set of edges
- Select a set of vertices
Edges
Select some edges from the graph.
graph._edges(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select a subset of the edges stored in the graph.
This is one of the entry points for the fluent AQL interface.
It will return a mutable AQL statement which can be further refined, using the
functions described below.
The resulting set of edges can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
In the examples the toArray function is used to print the result.
The description of this function can be found below.
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._edges().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1358448769",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1358710913",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1359104129",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/charlyAndDiana",
"_key" : "charlyAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1358907521",
"_from" : "male/charly",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._edges().toArray();
To request filtered edges:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._edges({type: "married"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1354844289",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/charlyAndDiana",
"_key" : "charlyAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1355303041",
"_from" : "male/charly",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._edges({type: "married"}).toArray();
Vertices
Select some vertices from the graph.
graph._vertices(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select a subset of the vertices stored in the graph.
This is one of the entry points for the fluent AQL interface.
It will return a mutable AQL statement which can be further refined, using the
functions described below.
The resulting set of edges can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
In the examples the toArray function is used to print the result.
The description of this function can be found below.
To request unfiltered vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._vertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1880901761",
"name" : "Diana"
},
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1880180865",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1880508545",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1880705153",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._vertices().toArray();
To request filtered vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1876576385",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1876904065",
"name" : "Bob"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]).toArray();
Working with the query cursor
The fluent query object handles cursor creation and maintenance for you. A cursor will be created as soon as you request the first result. If you are unhappy with the current result and want to refine it further you can execute a further step in the query which cleans up the cursor for you. In this interface you get the complete functionality available for general AQL cursors directly on your query. The cursor functionality is described in this section.
ToArray
Returns an array containing the complete result.
graph_query.toArray()
This function executes the generated query and returns the
entire result as one array.
ToArray does not return the generated query anymore and
hence can only be the endpoint of a query.
However keeping a reference to the query before
executing allows to chain further statements to it.
Examples
To collect the entire result of a query toArray can be used:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1455442049",
"name" : "Diana"
},
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1454721153",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1455048833",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1455245441",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.toArray();
HasNext
Checks if the query has further results.
graph_query.hasNext()
The generated statement maintains a cursor for you.
If this cursor is already present hasNext() will
use this cursors position to determine if there are
further results available.
If the query has not yet been executed hasNext()
will execute it and create the cursor for you.
Examples
Start query execution with hasNext:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.hasNext();
true
Iterate over the result as long as it has more elements:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> while (query.hasNext()) {
........> var entry = query.next();
........> // Do something with the entry
........> }
Next
Request the next element in the result.
graph_query.next()
The generated statement maintains a cursor for you.
If this cursor is already present next() will
use this cursors position to deliver the next result.
Also the cursor position will be moved by one.
If the query has not yet been executed next()
will execute it and create the cursor for you.
It will throw an error of your query has no further results.
Examples
Request some elements with next:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1423001729",
"name" : "Diana"
}
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1422280833",
"name" : "Alice"
}
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1422608513",
"name" : "Bob"
}
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1422805121",
"name" : "Charly"
}
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.next();
arangosh> query.next();
arangosh> query.next();
arangosh> query.next();
The cursor is recreated if the query is changed:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1426606209",
"name" : "Diana"
}
arangosh> query.edges();
[ GraphAQL social
.vertices()
.edges() ]
arangosh> query.next();
{
"_id" : "relation/charlyAndDiana",
"_key" : "charlyAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1427392641",
"_from" : "male/charly",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "married"
}
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.next();
arangosh> query.edges();
arangosh> query.next();
Count
Returns the number of returned elements if the query is executed.
graph_query.count()
This function determines the amount of elements to be expected within the result of the query.
It can be used at the beginning of execution of the query
before using next() or in between next() calls.
The query object maintains a cursor of the query for you.
count() does not change the cursor position.
Examples
To count the number of matched elements:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices();
arangosh> query.count();
4
Fluent queries
After the selection of the entry point you can now query your graph in a fluent way, meaning each of the functions on your query returns the query again. Hence it is possible to chain arbitrary many executions one after the other. In this section all available query statements are described.
Edges
Select all edges for the vertices selected before.
graph_query.edges(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select all edges for each of the vertices selected
in the step before.
This will include inbound as well as outbound edges.
The resulting set of edges can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
The complexity of this method is O(n*m^x) with n being the vertices defined by the
parameter vertexExamplex, m the average amount of edges of a vertex and x the maximal depths.
Hence the default call would have a complexity of O(n*m);
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered edges:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1372866689",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1373128833",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1372866689",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1373522049",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges().toArray();
To request filtered edges by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges({type: "married"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1369262209",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1369262209",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges({type: "married"}).toArray();
To request filtered edges by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1365657729",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1365919873",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1365657729",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1366313089",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.edges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
OutEdges
Select all outbound edges for the vertices selected before.
graph_query.outEdges(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select all outbound edges for each of the vertices selected
in the step before.
The resulting set of edges can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered outbound edges:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1437812865",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1438075009",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1438468225",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges().toArray();
To request filtered outbound edges by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges({type: "married"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1434208385",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges({type: "married"}).toArray();
To request filtered outbound edges by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1430603905",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1430866049",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1431259265",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.outEdges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
InEdges
Select all inbound edges for the vertices selected before.
graph_query.inEdges(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select all inbound edges for each of the vertices selected
in the step before.
The resulting set of edges can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered inbound edges:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1408911489",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges().toArray();
To request filtered inbound edges by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges({type: "married"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1405307009",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges({type: "married"}).toArray();
To request filtered inbound edges by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1401702529",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Bob"}]);
arangosh> query.inEdges([{type: "married"}, {type: "friend"}]).toArray();
Vertices
Select all vertices connected to the edges selected before.
graph_query.vertices(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select all vertices for each of the edges selected
in the step before.
This includes all vertices contained in _from as well as _to attribute of the edges.
The resulting set of vertices can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1487161473",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1487489153",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1487882369",
"name" : "Diana"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1487685761",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices().toArray();
To request filtered vertices by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices({name: "Alice"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1483556993",
"name" : "Alice"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices({name: "Alice"}).toArray();
To request filtered vertices by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Charly"}]).toArray();
[ ]
FromVertices
Select all source vertices of the edges selected before.
graph_query.fromVertices(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select the set of vertices where the edges selected
in the step before start at.
This includes all vertices contained in _from attribute of the edges.
The resulting set of vertices can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered source vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1389840513",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1390364801",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices().toArray();
To request filtered source vertices by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices({name: "Alice"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1386236033",
"name" : "Alice"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices({name: "Alice"}).toArray();
To request filtered source vertices by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Charly"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1382631553",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1383155841",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.fromVertices([{name: "Alice"}, {name: "Charly"}]).toArray();
ToVertices
Select all vertices targeted by the edges selected before.
graph_query.toVertices(examples)
Creates an AQL statement to select the set of vertices where the edges selected
in the step before end in.
This includes all vertices contained in _to attribute of the edges.
The resulting set of vertices can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
To request unfiltered target vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1465862273",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1466255489",
"name" : "Diana"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().toArray();
To request filtered target vertices by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices({name: "Bob"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1462257793",
"name" : "Bob"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices({name: "Bob"}).toArray();
To request filtered target vertices by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices([{name: "Bob"}, {name: "Diana"}]).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1458653313",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1459046529",
"name" : "Diana"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices([{name: "Bob"}, {name: "Diana"}]).toArray();
Neighbors
Select all neighbors of the vertices selected in the step before.
graph_query.neighbors(examples, options)
Creates an AQL statement to select all neighbors for each of the vertices selected
in the step before.
The resulting set of vertices can be filtered by defining one or more examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
@PARAM{options, object, optional}
An object defining further options. Can have the following values:
- direction: The direction of the edges. Possible values are outbound, inbound and any (default).
- edgeExamples: Filter the edges to be followed, see Definition of examples
- edgeCollectionRestriction : One or a list of edge-collection names that should be considered to be on the path.
- vertexCollectionRestriction : One or a list of vertex-collection names that should be considered on the intermediate vertex steps.
- minDepth: Defines the minimal number of intermediate steps to neighbors (default is 1).
- maxDepth: Defines the maximal number of intermediate steps to neighbors (default is 1).
Examples
To request unfiltered neighbors:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1419200641",
"name" : "Charly"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1419004033",
"name" : "Bob"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors().toArray();
To request filtered neighbors by a single example:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors({name: "Bob"}).toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1415399553",
"name" : "Bob"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors({name: "Bob"}).toArray();
To request filtered neighbors by multiple examples:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.vertices([{name: "Bob"}, {name: "Charly"}]).toArray();
[ ]
Restrict
Restricts the last statement in the chain to returnonly elements of a specified set of collections
graph_query.restrict(restrictions)
By default all collections in the graph are searched for matching elements
whenever vertices and edges are requested.
Using restrict after such a statement allows to restrict the search
to a specific set of collections within the graph.
Restriction is only applied to this one part of the query.
It does not effect earlier or later statements.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{restrictions, array, optional}
Define either one or a list of collections in the graph.
Only elements from these collections are taken into account for the result.
Examples
Request all directly connected vertices unrestricted:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.edges().vertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1476348033",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1476675713",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1476348033",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1476872321",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.edges().vertices().toArray();
Apply a restriction to the directly connected vertices:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.edges().vertices().restrict("female").toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1447577729",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1447577729",
"name" : "Alice"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.edges().vertices().restrict("female").toArray();
Restriction of a query is only valid for collections known to the graph:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.edges().vertices().restrict(["female", "male", "products"]).toArray();
[ArangoError 10: vertex collections: products are not known to the graph]
Filter
Filter the result of the query
graph_query.filter(examples)
This can be used to further specfiy the expected result of the query.
The result set is reduced to the set of elements that matches the given examples.
@PARAMS
@PARAM{examples, object, optional}
See Definition of examples
Examples
Request vertices unfiltered:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1473071233",
"name" : "Bob"
},
{
"_id" : "female/diana",
"_key" : "diana",
"_rev" : "1473464449",
"name" : "Diana"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().toArray();
Request vertices filtered:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().filter({name: "Alice"}).toArray();
[ ]
Request edges unfiltered:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().outEdges().toArray();
[
{
"_id" : "relation/bobAndDiana",
"_key" : "bobAndDiana",
"_rev" : "1470843009",
"_from" : "male/bob",
"_to" : "female/diana",
"type" : "friend"
}
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().outEdges().toArray();
Request edges filtered:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._edges({type: "married"});
arangosh> query.toVertices().outEdges().filter({type: "married"}).toArray();
[ ]
Path
The result of the query is the path to all elements.
graph_query.path()
By defaut the result of the generated AQL query is the set of elements passing the last matches.
So having a vertices() query as the last step the result will be set of vertices.
Using path() as the last action before requesting the result
will modify the result such that the path required to find the set vertices is returned.
Examples
Request the iteratively explored path using vertices and edges:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.outEdges().toVertices().path().toArray();
[
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1443973249",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndBob",
"_key" : "aliceAndBob",
"_rev" : "1445021825",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/bob",
"type" : "married"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1444300929",
"name" : "Bob"
}
],
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1443973249",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "relation/aliceAndCharly",
"_key" : "aliceAndCharly",
"_rev" : "1445283969",
"_from" : "female/alice",
"_to" : "male/charly",
"type" : "friend"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1444497537",
"name" : "Charly"
}
]
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.outEdges().toVertices().path().toArray();
When requesting neighbors the path to these neighbors is expanded:
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors().path().toArray();
[
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1440368769",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/charly",
"_key" : "charly",
"_rev" : "1440893057",
"name" : "Charly"
}
],
[
{
"_id" : "female/alice",
"_key" : "alice",
"_rev" : "1440368769",
"name" : "Alice"
},
{
"_id" : "male/bob",
"_key" : "bob",
"_rev" : "1440696449",
"name" : "Bob"
}
]
]
arangosh> var examples = require("org/arangodb/graph-examples/example-graph.js");
arangosh> var graph = examples.loadGraph("social");
arangosh> var query = graph._vertices({name: "Alice"});
arangosh> query.neighbors().path().toArray();

